Mak Or Kms License
Volume License Keys (VLK), including MAK and KMS, are issued to you under a specific license agreement and enable your organization to use the software that you have licensed. There is retail that takes retail keys There is OEM, that takes OEM keys and there is Volume License that takes KMS and MAK keys? That correct? Reason why i'm asking is because I just installed server 2008, and it is in Initial Grace Period, according to slmgr.vbs -dli command.
In software licensing, a volume licensing is the practice of selling a license authorizing one computer program to be used on a large number of computers or by a large number of users. Customers of such licensing schemes are typically business, governmental or educational institutions, with prices for volume licensing varying depending on the type, quantity and applicable subscription-term. For example, Microsoft software available through volume-licensing programs includes Microsoft Windows, Microsoft Office.[1][2]
Traditionally, a volume licensing key (VLK), which could be supplied to all instances of the licensed computer program, was involved in volume licensing. With the popularity of the software as a service practices, volume licensing customers only supply their software with credentials belonging to an online user account instead, which is used for other aspects of services and provisioning.
- 2Notable examples
- 3Unauthorized use
Overview[edit]
Traditionally, a product key has been supplied with computer programs. It acts analogously to a password: The computer programs of the old ask the user to prove their entitlement; in response, the user provides this key. This key, however, must only be used once, i.e. on one computer. A volume licensing key (VLK), however, can be used on several computers. Vendors can take additional steps to ensure that their products' key are only used in the intended number. These efforts are called product activation.
Volume licenses are not always transferable. For example, only some types of Microsoft volume license can be transferred, provided a formal transfer process is completed, which enables Microsoft to register the new owner. A very small number of software vendors specialize in brokering such transfers in order to allow the selling of volume licenses and keys. The most notable of these, Discount-Licensing, pioneered the sale of Microsoft volume licenses in this way.[3]
Notable examples[edit]
Microsoft[edit]
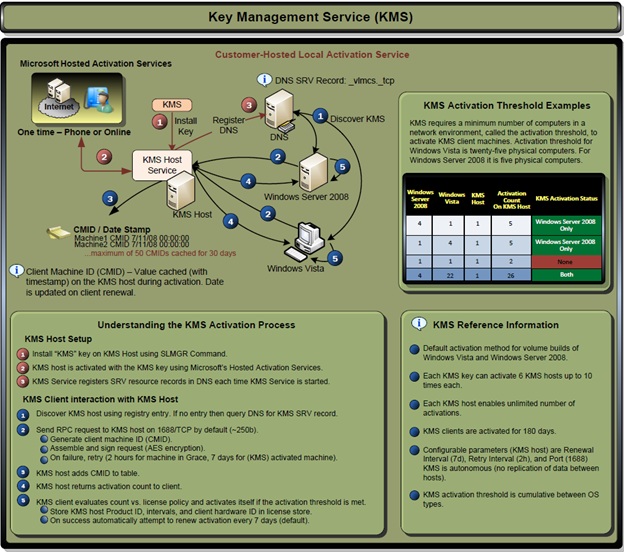
Microsoft has been engaged in volume licensing since its inception, as the enterprise sector is its primary market. With the release of Windows XP in 2001, Microsoft introduced Microsoft Product Activation, a digital rights management (DRM) scheme to curb software piracy among consumers by verifying the user's entitlement to the product license. At the time, however, the volume-licensed versions of Windows XP were exempt from this measure. (See § Unauthorized use.) Starting with Windows Vista, Microsoft introduced two volume licensing methods for IT professionals in charge of installing Windows in organizations, both of which are covered by Microsoft Product Activation: The first is Multiple Activation Keys (MAK), which are the same as Windows XP's volume licensing keys but require product activation. The second is Key Management Server (KMS) and its corresponding keys. Hosts activated via a KMS have to report back to a software license server once every 180 days.[4][5] Licenses using these schemes can be procured via the Microsoft Software Assurance program.
A large group of Microsoft customers are OEMs that assemble and sell computers, such as desktops, laptops, tablet computers and mobile device. In the devices sold by these OEMs, Windows license data is stored in the computer's BIOS in an area referred to as the 'ACPI_SLIC', so that KMS can detect the use of previous Microsoft products even with the storage device removed or erased.[6] For Windows Vista and Windows 7, the SLIC data are complementary; a volume licensing product key is still supplied with the device, which the user needs in the event of reinstalling Windows. Starting with Windows 8, however, everything needed to authorize the device is stored with SLIC data.
In 2010, Microsoft introduced the Office 365 licensing program. in which Microsoft Office, Microsoft Exchange Server and Skype for Business Server products are licensed based on the software as a service (SaaS) model: In exchange for a monthly subscription fee, software, its updates, support for them, provisioning, administration, licensing and additional services are all provided through an online web-based dashboard. In this scheme, licensed apps communicate recurrently with Microsoft over the Internet; as such, a product key needs not be issued to the user. Instead the administrator needs to sign up for Microsoft account, which holds details such as licensed apps, their number, and payment methods. This account is protected by credentials such as a username and a password.
Adobe[edit]
Introduced in 2011, Adobe Creative Cloud is a SaaS offering in which software produced by Adobe, their updates, support for them, provisioning, administration, licensing and additional services are all provided over the Internet, in exchange for a monthly subscription fee. As with the Office 365, a user account registered with Adobe is all that is required to authorize software and store payment information.
Unauthorized use[edit]
Microsoft has blocked several volume license keys that have been abused in service packs, starting with Windows XP Service Pack 1. Microsoft even developed a new key verification engine for Windows XP Service Pack 2 that could detect illicit keys, even those that had never been used before. Several security consultants have condemned the move by Microsoft, saying that leaving a large install base unpatched from various security holes is irresponsible because this unpatched install base can be leveraged in large scale Internet attacks, such as Trojan horses used to send spam e-mail. Others have come to Microsoft's defense, arguing that Microsoft should not have to provide support for illegal users. After much public outcry, Microsoft elected to disable the new key verification engine. Service Pack 2 only checks for the same small list of commonly used keys as Service Pack 1. Users of existing installations of Windows XP can also change their product key by following instructions from Microsoft.[7]
Leaked keys[edit]
A volume license key that was commonly used to bypass product activation in early versions of Microsoft's Windows XP operating system was FCKGW-RHQQ2-YXRKT-8TG6W-2B7Q8.[8] This key was part of the first warez release of the final version of Windows XP by a group called devils0wn, 35 days before the official retail release on 28 August 2001.[9] The key is now obsolete, as it has been blacklisted by Microsoft since August 2004, and affected computers will display a WGA notification.[10] It was made famous partly because it featured in a popular image circulated on the Internet before the retail launch of Windows XP. In the image, the key is written on a CD-R containing the leaked operating system and held in front of a digital Microsoft sign counting down the days until the release of Windows XP.[11]
Users using these keys will receive an error message when they install the latest service pack, and such users are told to obtain a legitimate license and change their product key.[12]
Public KMS servers[edit]
Any client machine with the correct KMS client setup keys can authenticate against any KMS server. KMS client keys are well known and documented publicly by Microsoft.[13] KMS servers require a minimum of 25 clients to properly activate, but also stop counting additional licenses beyond 50, and automatically accept any client key once reaching the 25 client threshold.
Businesses operating KMS servers are required to properly shield the KMS server behind firewalls so that it cannot be reached from the Internet, and be used to authorize illegal use of KMS client keys by the general public. Public exposure of a KMS server can result in Microsoft revoking the server key, thereby disabling all attaching clients.
External KMS server access is desirable for devices on long-term leave away from the corporate network, as KMS client activation will expire after six months of not being able to contact a KMS server. For this situation, a business can make it accessible through a virtual private network (VPN) known only to the devices outside the corporate network.
KMS server and client emulators[edit]
An unofficial KMS server emulator exists that will activate Windows or Office even if the software was not licensed or paid for, regardless of whether or not there are 25 or more computers on the network, and regardless of whether or not a previous version of Windows was installed.[14] There is also a program that will send KMS requests to a legitimate KMS server, in order to fool the server into thinking that there are 25 or more computers on the network. Microsoft considers both of these exploits to be a violation of the Terms and Conditions.[15]
References[edit]
- ^Lowe, Doug (2008). Networking All-in-One Desk Reference For Dummies (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 205–206. ISBN9780470333884.
- ^Microsoft. 'Microsoft Volume Licensing'. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ^'Second-Hand Software Licences for Sale (And They're Legal)'. Out-Law.com. Pinsent Masons. 9 November 2005. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- ^Top 7 Things You Should Know About Activation and Genuine Windows (PowerPoint, referred from Windows Activation | Genuine Windows 7, Vista, XP | TechNet)
- ^'Windows Activation Technologies in Windows 7'. Technet.Microsoft.com.
- ^'Windows 7 Activation Can Fail Due to BIOS ACPI_SLIC table Issues'. Softpedia. 3 August 2010. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^Microsoft Help and Support: How to change the product key at the time of activation
- ^bit-tech.net: Microsoft outlines Vista piracy plans, Published on 5 October 2006 by Wil Harris
- ^'[iSONEWS] KMSAuto Lite - Microsoft Windows 10 Activator'. Archived from the original on 22 June 2018.
- ^arstechnica.com: Windows Genuine Advantage for dummies By Matt Mondok | Last updated 29 November 2006 6:19 PM
- ^'More on the FCKGW-RHQQ2-YXRKT-8TG6W-2B7Q8!'. HarshJ.com. 19 March 2007. Archived from the original on 21 June 2014. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^'TechRepublic Get IT Done: Change the Product Key on Windows XP'. Articles.TechRepublic.com.[permanent dead link]
- ^Volume activation: Plan for volume activation: Appendix A: KMS Client Setup Keys, Published: 24 August 2012, Updated: 16 July 2014, https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj612867.aspx
- ^'Microsoft Toolkit - Official KMS Solution for Microsoft Products'. Archived from the original on 3 August 2015.
- ^'Microsoft Campus-Agreement End-User License-Agreement'.
You may not use different versions of different components, such as server software and additional software, unless the license terms for the product expressly permit you to do so.
External links[edit]
Applies to:Volume licensed versions of Office 2019 and Office 2016, including Project and Visio
Multiple Activation Key (MAK) activation is used for one-time activation through Microsoft-hosted activation services, either via the internet or by telephone. MAK activation requires that a MAK is installed on a client computer and instructs that computer to activate itself against those services.
Each MAK has a predetermined number of allowed activations and is based on your volume licensing agreement. Each Office activation that uses MAK counts toward the activation limit. After Office is activated, no re-activation is required unless the hardware changes significantly.
There are two ways to activate computers by using MAK:
MAK independent activation requires that each computer independently connect and be activated with Microsoft, either over the Internet or by telephone. MAK independent activation is best for computers that have direct access to the internet.
MAK proxy activation by using VAMT enables one computer with internet access to process activation requests on behalf of multiple computers. MAK proxy activation is configured by using the Volume Activation Management Tool (VAMT). MAK proxy activation is appropriate for environments in which security concerns might restrict direct access to the internet or to development and test labs. For more information, see Perform Proxy Activation.
Activate Office 2019 by using MAK
If you're using MAK to activate volume licensed versions of Office 2019, you specify the key in the configuration.xml file used by the Office Deployment Tool when you deploy Office 2019 to the users in your organization. For more information, see Deploy Office 2019 (for IT Pros).
Activate Office 2016 by using MAK
If you're using MAK to activate volume licensed versions of Office 2016, you can enter the key by using one of the following supported methods:
Before you install Office 2016, you can use the Office Customization Tool (OCT) or the Config.xml file.
After you install Office 2016, you can use the product UI, the Volume Activation Management Tool (VAMT), the ospp.vbs script, or enable a non-admin user to activate using MAK.
Configure MAK activation in the Office Customization Tool (OCT)
To enter a MAK key by using the Office Customization Tool (OCT), follow these steps:
In the OCT, go to the Licensing and user interface page.
Select Enter another product key, and then in the Product key field, enter the multiple activation key (five sets of five numbers or characters).
After making any other necessary changes in the OCT, save the .msp file in the Updates folder.
Note
- For more information, see Office Customization Tool (OCT) 2016 Help: Overview and Office Customization Tool (OCT) 2016 Help: Licensing and user interface.
- You can activate Office 2016 automatically when you install by setting the AUTO_ACTIVATE property value to 1 in the Config.xml file. For more information, see Setting element. (Even though this article is for an earlier version of Office, the information also applies to Office 2016.)
Configure MAK activation in the Config.xml file
To enter a multiple activation key by using the Config.xml file, follow these steps:
- Add the following line to the Config.xml file:
Replace AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDDEEEEE with your 25-character product key.
- To apply the settings in Config.xml, at a command prompt, type the following command, and then press ENTER:
Note
- For more information about the Config.xml file, see Config.xml file reference. (Even though this article is for an earlier version of Office, the information also applies to Office 2016.)
- You can activate Office 2016 automatically when you install by setting the AUTO_ACTIVATE property value to 1 in the Config.xml file. For more information, see Setting element. (Even though this article is for an earlier version of Office, the information also applies to Office 2016.)

Windows License Mak Vs Kms
Change the key by using the product UI
To change the Office 2016 product key on only one computer:
- Open an Office 2016 application, such as Word.
- Go to File > Account.
- Choose Change Product Key and enter the product key.
If you need to change the Office 2016 product key on multiple computers after Office is installed, we recommend that you use Volume Activation Management Tool (VAMT) 3.1. For more information, see Volume Activation Management Tool (VAMT) Technical Reference.
Enable a non-admin user to activate an Office by using MAK
An administrator can create a registry key that allows a standard user (that is, a user who isn't an administrator) to activate Office 2016 by using MAK. By default, volume licensed versions of Office 2016 disable this behavior.
This can be used if you want a user to manually activate Office by using MAK, replace an existing key with a new key, or switch from KMS to MAK activation.
To enable this behavior, add the following line to the Config.xml file:
Or, you can set the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftOfficeSoftwareProtectionPlatform registry key to enable or disable standard user activation
- To enable, set 'UserOperations'=dword:00000001
- To disable, set 'UserOperations'=dword:00000000
Note
For more information about the Config.xml file, see Config.xml file reference. (Even though this article is for an earlier version of Office, the information also applies to Office 2016.)